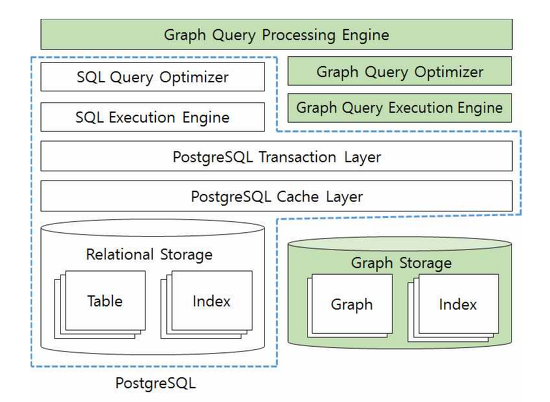
Architecture
AgensGraph is a multi-model database developed on the basis of PostgreSQL. AgensGraph is designed to offer all the features provided by PostgreSQL and process graph queries using Cypher, a graph query language. Internally, they are largely divided into the PostgreSQL processor and the Graph processor, both of which jointly use cache and transaction areas. Users may take advantage of better performance and more convenient implementation by simultaneously performing SQL and Cypher queries on a single query.
Process structure
AgensGraph uses the same client/server model as PostgreSQL. A session (work) consists of the following interacting processes (programs):
Server process
Manages database files, processes (accepts or rejects) the requests made by client applications to connect to the server, and prepares base work to enable clients to use the database. The name of this process is postgres.
Client process
Refers to user-side applications that need to access the database. There are a wide range of client applications, understandably: text-based programs, graphical applications, or, in some cases, web pages that can be shown through a web server. Some client programs are included in the distribution packages. Most of such applications are developed by users.
As is often the case with programs in a client/server environment, AgensGraph also allows the client and server to be different hosts. In this case, communications between them are made mostly under the TCP/IP network infrastructure- a point we should clearly understand; if the client and server are different, the client cannot directly access a database file it wants. In other words, a file that can be accessed by the client is a file on the host where the client is running, not a file on the host where the server is running.
For concurrent access by users, the AgensGraph server creates a new process for each connection. This means that when a client and a newly created server process communicate, the communication is done without intervention by postgres (master process). Simply put, postgres is always running on the server host to process the clients’ connection requests and create new child server processes.